Understanding Gum Recession: Symptoms, Risks, and Treatment
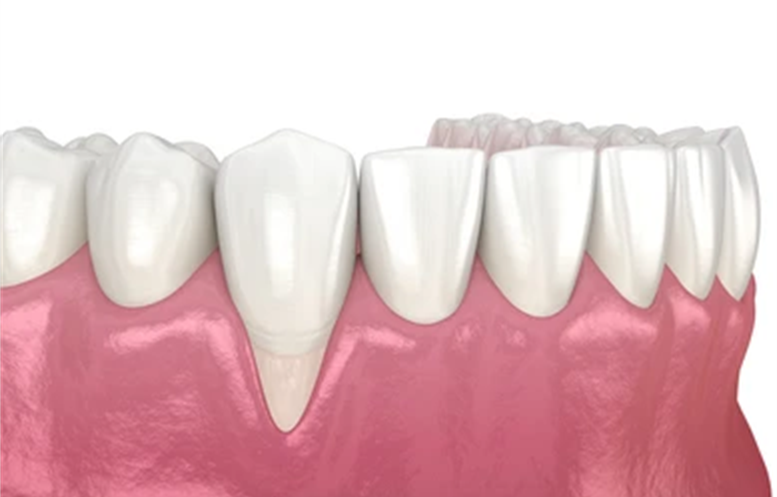
Gum recession is one of the most common complaints/issues we see in our patients at Spokane Dental. Oftentimes people will notice increased tooth sensitivity, or that their teeth appear “longer” when they smile. These can be early signs of gum recession- where the gum tissue surrounding the teeth recedes, exposing more of the tooth enamel or even the tooth's root (called dentin). Our team at Spokane Dental focuses so much on prevention when it comes to oral and overall health. In today’s post we will talk about recognizing the symptoms, understanding the causes, and knowing the risks of gum recession so we can help you protect your smile for years to come.
What is Gum Recession?
Gum recession occurs when the gums gradually pull away from the tooth's surface, which can expose sensitive tooth roots to bacteria and plaque buildup. It’s often a slow process, but it can lead to significant discomfort and more severe dental issues over time. When the gums (or gingiva) begin to recede, the bone and ligaments surrounding the teeth (the peridontium) also resorb. We call this periodontitis, and it puts the teeth at risk.
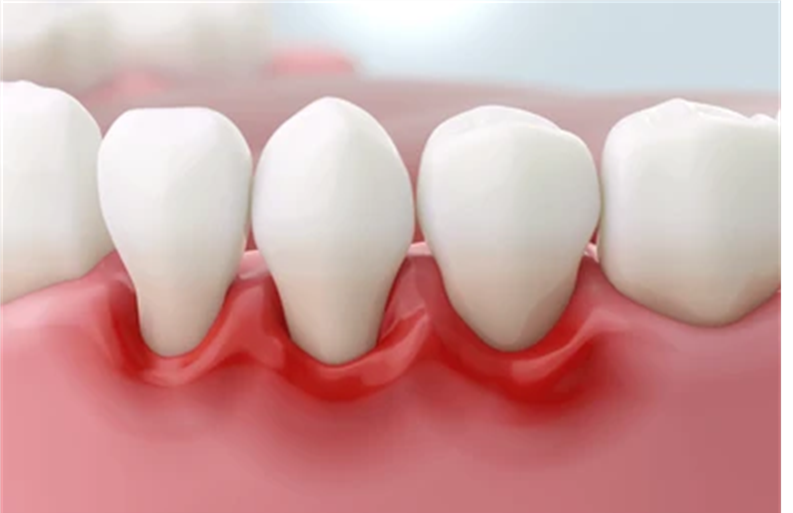
Symptoms of Gum Recession
Some early signs of gum recession can be subtle, but recognizing them can help prevent further gum loss. Common signs include:
- Sensitivity: Exposed roots can cause heightened sensitivity, particularly to hot or cold foods and drinks.
- “Longer Teeth” Appearance: As gums recede, teeth may appear longer.
- Visible Root Surfaces: The roots of your teeth may become visible, especially if recession has progressed.
- Loose Teeth: In severe cases, gum recession causes significant bone resorption, leading to loose teeth.
- Bleeding Gums: If your gums bleed when brushing or flossing, it could be a sign of gum disease (gingivitis), which often precedes gum recession.
Causes of Gum Recession
Several factors can contribute to gum recession, including:
- Aggressive Brushing: Brushing with too much pressure or using a hard-bristled toothbrush can wear down gum tissue and even enamel.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to plaque and tartar buildup, which causes an inflammatory response in the gums and leads to recession.
- Genetics: Some people may be genetically predisposed to thinner gum tissue, which can increase the likelihood of recession.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels, particularly in women, can make gums more sensitive and vulnerable to recession.
- Teeth Grinding and Clenching: Grinding or clenching puts pressure on the teeth and gums, which can cause recession over time.
- Tobacco Use: Smoking and chewing tobacco products can damage gum tissue, increasing the risk of gum disease and recession.
Risks Associated with Gum Recession
Gum recession can lead to several oral health problems if left untreated:
- Increased Risk of Decay: The dentin (root surface of the tooth) is softer than enamel and more vulnerable to decay.
- Gum Disease: Gum recession can be both a symptom and a cause of periodontal disease, which can ultimately lead to tooth loss.
- Bone Loss: As gums recede and bacterial infections develop, the bone supporting the teeth can resorb.
- Tooth Loss: Advanced gum recession weakens the bone and ligaments holding the teeth in place, leading to tooth mobility and potential loss.
Preventing Gum Recession
Preventing gum recession requires a proactive approach to oral care and attention to any changes in your gums. Here are some effective ways to protect your gums:
- Practice Gentle Brushing: Use a soft or extra-soft bristled toothbrush and brush in gentle, circular motions angled 45 degrees towards the gum line.
- Floss Regularly: Flossing once a day removes plaque between teeth and along the gumline, reducing the risk of gum disease.
- Visit Dr. Smith: Regular dental check-ups and cleanings can help detect early signs of gum recession and other oral health issues.
- Wear a Nightguard: If you grind your teeth at night, we can make you a custom nightguard that protects your gums.
- Quit Smoking: Reducing or eliminating tobacco use can significantly lower the risk of gum disease and recession.
Treatment Options for Gum Recession
If you’re experiencing gum recession, several treatment options are available to help restore your gum health:
- Scaling and Root Planing: A “deep cleaning” procedure from our hygieniests that removes plaque and tartar from below the gumline, allowing the gums to heal.
- Gum Grafts: In more severe cases, a gum graft may be necessary to restore lost gum tissue. This is a procedure we would refer you to a periodontist to discuss.
- Pinhole Surgical Technique: A minimally invasive procedure where the gum is gently repositioned to cover exposed roots without the need for sutures.
- Desensitizing Agents: We may apply special agents to help reduce sensitivity in areas where gum tissue is thinner or where roots are exposed.
When to give us a call
If you notice any symptoms of gum recession, scheduling an appointment with Spokane Dental is essential. Early intervention can prevent the progression of recession and protect your teeth from further damage. At Spokane Dental, we provide comprehensive gum care and personalized treatment plans to keep your gums healthy and your smile looking its best.
Gum recession is more than just a cosmetic issue—it’s a serious oral health concern that can lead to tooth loss and other complications if untreated. Taking steps to protect your gums and visiting your dentist regularly are essential in preventing and managing gum recession. At Spokane Dental, we’re committed to providing you with the best possible care to keep your smile healthy and strong. Give us a call today at (509) 822-5614 to schedule!
Photo Credits:

